How To Sleep Better: Tips + Common Impacts on Your Sleep
You can sleep better by practicing healthy nighttime habits. This includes maintaining a consistent schedule, avoiding too much caffeine, and making sure you have a comfortable and quiet place to get some much-needed rest. You should also avoid some bad practices that prevent you from relaxing at night.
In this article, we’ll share things to know about these good and bad sleep habits. If you've ever wondered what to do at night when you can't sleep, we'll share a few tried-and-tested methods that could help you sleep better and faster.
How Can I Get A Better Night’s Sleep?
To get a better night’s sleep, you need to have healthy sleep habits. Listen to your body clock, don’t eat large meals before bedtime, get regular exercise, and avoid bright light in the evening. It’s also a good idea to invest in a comfortable mattress, bedding, and pillow.
Why Does Sleep Matter So Much For Health And Well-Being?
Sleep matters a lot for our health and well-being for the following reasons:
Strengthens Your Immune System
During sleep, the immune system releases protective proteins called cytokines, which are essential for fighting infections and stress. You may also lose antibodies and cells if you don’t get enough restful sleep.
Promotes Better Mental Health
The different stages of sleep play a role in brain health. By getting a good night’s sleep, you can learn better, remember well, and think clearly.
Helps Regulate One’s Weight
People who suffer from sleep deprivation are more likely to have a higher body mass index (BMI) and be more prone to obesity. To compensate for the lack of good-quality sleep, people tend to experience increased hunger and food cravings. Aside from that, people may experience salt retention and decreased levels of leptin and insulin sensitivity.
What Can Affect Your Sleep?
Consuming caffeine, smoking, and reading stimulating content at night can affect your sleep. You should avoid these bad habits because a single bad night’s sleep can disrupt your energy and mood the next day. Not only that, but a pattern of poor sleep can also start to take a toll on your life.
7 Things That Can Really Mess with Your Sleep
Here are more details on the most common causes of sleep deprivation:
- Consuming caffeine in the evening
- Smoking before bed
- Charging electronics in your bedroom
- Taking medications and supplements
- Reading stimulating content before sleep
- Being too warm
- Eating or drinking at night
According to the National Sleep Foundation, most adults need seven to nine hours of sleep each night. Your personal needs may vary, but you should always make sleep a top priority. Don’t let bad sleep habits stand in the way of a great night’s sleep.
If you find you’re not sleeping well, all is not lost. You can learn how to sleep better. Eliminating factors that disrupt sleep should be your first step. You can also take positive steps to promote better sleep. But if all your efforts fail, don’t hesitate to talk to a specialist about your sleep problems.
Consuming Caffeine In The Evening
Many of us start our mornings with a cup of coffee or tea. We all know that a little caffeine can provide a pick-me-up when our energy sags. And a warm beverage can feel calming and soothing.
Although a cup of coffee after dinner can seem appealing, be mindful of caffeine. If you consume a caffeinated beverage in the evening, your sleep can suffer. Remember that cold drinks like sodas and iced teas can contain caffeine, too.
Want to indulge in a favorite beverage and fall asleep easily? Try something decaffeinated. Many decaf coffees are very appealing, and herbal teas can be a delight. Some teas containing chamomile, lavender, lemon balm, or valerian root can actually help you fall asleep.
Smoking Before Bed
Smoking can lead to many poor health outcomes, and it can also disrupt your sleep. Never forget that nicotine is a stimulant. If you smoke within two hours before bed, you’re likely to have issues falling asleep.
Over time, the stimulating qualities of nicotine can disrupt a smoker’s sleep patterns. Smoking changes your circadian rhythm, which is your internal clock that affects your sleep-wake cycle. Many smokers suffer from sleep disorders, particularly insomnia.
Do you smoke and want to know how to sleep better? Cutting back or stopping smoking entirely may be the key to more restful nights.
Charging Electronics In Your Bedroom
Today, smartphones are necessities for most people. But far too many people bring their electronic devices into their bedrooms. Using electronics before bed can short-circuit your internal clock and suppress the release of melatonin.
Why does this happen? Most devices emit blue light. Although blue light is beneficial during the day, it’s disruptive to us at night. If you use a white noise machine, make sure it doesn’t emit any light.
You’ve likely already heard about the connection between poor sleep and electronics. You may even be patting yourself on the back for curbing the urge to check social media or send emails before bed. But you should know that charging your device on your nightstand can also mess with your sleep.
Even the small indicator light that shows your device is charging can disturb your sleep. If those lights are blue, they can cause even more problems. Your best bet: charge your devices during the day or in another room away from your sleep space.
Taking Medications And Supplements
Do you take prescriptions or supplements every day? You may prefer to take them in the evenings, but you could be harming your sleep. Certain medications, like steroids and some B vitamins, can cause sleep disruptions. Of course, other medicines may have a sleep-inducing effect. Always check with your healthcare provider to find out the best time to take meds or vitamins every day.
Also, be careful with sleep supplements, including melatonin. Often, you’ll develop a tolerance for these substances and need to take more and more. Over time, you may find that a sleep aid no longer works for you. Instead of inducing sleep, it can actually keep you awake. Avoid this problem by taking the smallest dose possible and using sleep supplements sparingly. Don’t rely on them to fall asleep every night.
Reading Stimulating Content Before Bed
Keeping a book on the nightstand is a tradition for many people. But research has shown that not all bedtime books are created equal. Some books may make it hard to fall asleep. The reason? They may be intellectually demanding and activate your brain instead of allowing it to rest. Books that excite you or bring up strong emotions can diminish sleep quality.
This fact doesn’t mean you need to entirely give up reading before bed. Instead, choose your reading material with care. Save the adventure novels and tear-jerker romances for daytime reading. Choose lighter topics at night.
Being Too Warm
It’s possible to be too cozy at night. If you snuggle under layers of blankets and cuddle with a partner, or have a memory foam mattress, it’s easy to get too hot. And this can disrupt sleep.
What’s the answer? Shed some blankets and skip the heavyweight PJs. Better yet, choose a cool and comfortable mattress like Purple. You can also lower your thermostat at night and save some cash during the winter months. Keep in mind that most adults have an ideal sleep temperature of 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit.
But don’t stray too far in the other direction. Being too cold can disrupt your sleep as well. Aim for the sleep temperature sweet spot and enjoy more Zzzs.
Eating And Drinking At Night
We all love an occasional bedtime snack or nightcap. In fact, some foods can help you sleep. Nutrition researchers suggest that a small snack of fewer than 150 calories before bed can be beneficial. But you should know that eating and drinking too much before bedtime can be a recipe for poor sleep.
Most nutritionists recommend avoiding eating for at least two to three hours before bedtime. This window gives time for your food to digest properly.
Why is this important? Lying down can cause reflux and heartburn, especially if you’ve consumed spicy or acidic foods. Consuming food can signal to your brain that it’s time to be awake, so it’s hard to get a night’s rest.
Drinking before bed can also make you need to get up and head into the bathroom. You may find it difficult to go back to sleep. A small cup of tea is likely fine, but don’t overdo it. The worst thing you can drink before bed is alcohol — which prevents you from getting the deep sleep (REM sleep) we all need.
How To Fall Asleep Faster And Sleep Better
To fall asleep faster and sleep better, you can try the following methods:
The Military Method
As its name suggests, the military method was developed by the US Navy Pre-Flight School. The goal was to help pilots fall asleep in two minutes or less so that they are always well-rested and ready for combat.
Here are the steps to the military method:
- Keep all your facial muscles relaxed, including the ones in your mouth.
- Release tension in your shoulders.
- Inhale, exhale, and relax your chest.
- Clear your head for 10 seconds. If needed, consciously tell yourself, “Don’t think.”
The 4-7-8 Breathing Method
This method involves simple breathing and counting techniques. Follow the steps below:
- Part your lips slightly, and exhale through your mouth.
- Close your mouth then inhale through your nose for four seconds. Exhale.
- Inhale again and hold your breath for seven seconds.
- Exhale forcefully for eight seconds.
- Repeat the cycle until you feel sleepy.
Note: If you already feel drowsy without completing the breathing cycles, feel free to let yourself fall asleep.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR)
This method tenses and relaxes the muscles, helping you settle into sleep. Follow these steps:
- Raise your eyebrows and tighten your forehead muscles.
- Relax your muscles, and wait for 10 seconds.
- Smile widely until you feel the tension in your cheeks. Hold the position for five seconds.
- Relax, and wait 10 seconds.
- Close your eyes, furrow your eyebrows, and squint. Hold for five seconds.
- Relax, and wait another 10 seconds.
- Flex your triceps, chest muscles, and feet, then relax them immediately. Pause for 10 seconds.
- Repeat the cycle until you feel sleepy.
Note: If you already feel drowsy without completing the tensing/relaxing cycles, feel free to let yourself fall asleep.
What Other Things Can I Do To Sleep Better?
If you want to sleep better, eliminating bad sleep habits is a great place to start. But there are many things you can do to promote a good night’s rest. Here are a few tips for anyone who wants to learn how to fall asleep faster.
Establish a Sleep Routine
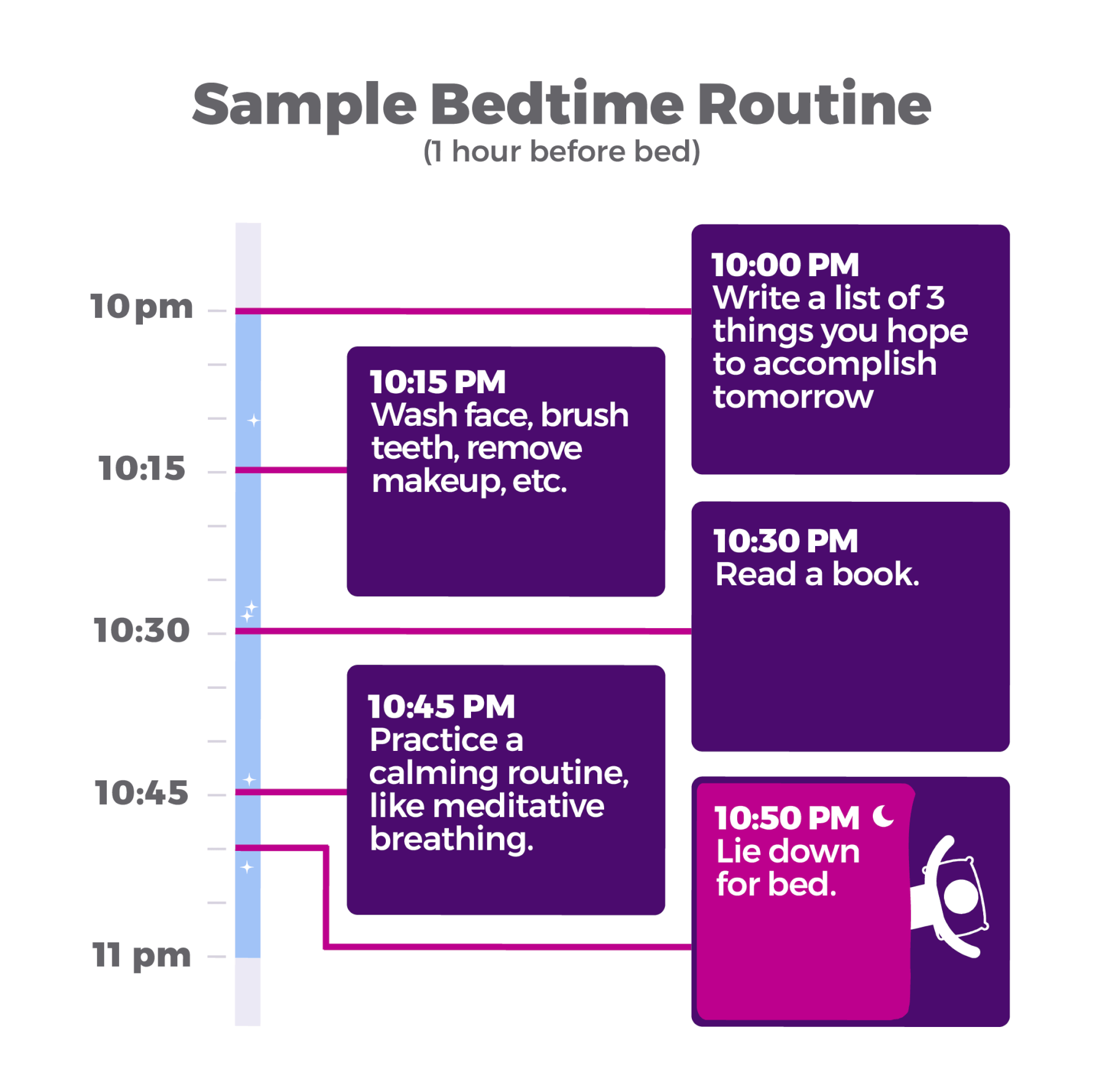
Consistency is essential for sleep. You should aim to go to bed at the same time and wake up at the same time every day – even on weekends. This sleep schedule will help regulate your body’s circadian rhythm and help you fall and stay asleep.
Practicing bedtime rituals can signal your brain and body that it’s time to sleep. Pick a sleep time when you’ll turn in and start your ritual 30-minutes earlier. Try things like a warm bath, a cup of relaxing tea, meditation, and journaling. Be sure to stay away from screens and gadgets for at least 60 to 90 minutes before bedtime.
Use Quality Mattresses, Pillows, And Bedding
Your mattress has a significant impact on how well you should sleep. First, consider whether you need a new mattress.
When it’s time for an update, choose a supportive, comfortable mattress. The right mattress provides immersive comfort while supporting your back and hips. If you have any issues with allergies, choose a hypoallergenic mattress to safeguard against allergens.
Pillows and bedding matter, too. Always choose a pillow that adapts to your head and neck for maximum comfort. Make sure your pillows are soft, yet able to retain their structure over time.
If you’re frequently tossing and turning at night or suffering from anxiety, select a weighted blanket. Studies have shown that weighted blankets can promote relaxation and support the release of sleep-inducing serotonin.
How To Sleep Better FAQs
What to drink to sleep faster?
Some drinks like chamomile tea, milk, and peppermint tea contain ingredients that can help you sleep faster. Here’s an overview of their benefits:
- Chamomile tea: Many people drink chamomile tea for its calming effects. It’s rich in flavonoids and terpenoids that help reduce anxiety, treat hysteria, and prevent nightmares.
- Ashwagandha tea: Ashwagandha tea can help the body relax and prepare for sleep. It’s available in teabags and may also be added to a glass of warm milk.
- Peppermint tea: Peppermint tea is often used to relieve stress and aid sleep. It may also help relieve symptoms of constipation and irritable bowel syndrome.
- Warm milk: Warm milk and dairy products have long been used to aid in improving sleep quality and duration. They also have anti-inflammatory components that may reduce joint pain from osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Almond milk: Almond milk is an excellent sleep aid for people who are avoiding milk or dairy products. It’s high in hormones that promote sleep, such as melatonin and magnesium.
Why can I not sleep at night?
An underlying health condition or bad sleep habits may be the reason you cannot sleep at night. Health conditions that affect your sleep include chronic pain, sleep apnea, and neuropathy.
Meanwhile, bad habits like taking too many daytime naps, eating heavy meals 1-2 hours before bedtime, and consuming too much caffeine can prevent you from getting restful sleep. These habits may also contribute to daytime sleepiness.
Another reason you are suffering from lack of sleep is the bedroom temperature. A comfortable temperature for sleep should be 60 to 67 degrees Fahrenheit (15.6 to 19.4 degrees Celsius).
What foods make you sleepy?
Turkey is one of the foods that can make you sleepy because it contains tryptophan, an essential amino acid that helps balance one’s mood. Aside from turkey, fatty fish like salmon and tuna contain vitamin D and omega-3, which help increase the production of serotonin.
Another type of food you should try to feel sleepy is kiwi. Daily consumption of kiwifruit before bedtime has been shown to help adults suffering from sleep disorders.
